Warning about black fungus Mucormycosis
- According to estimates by the US Centers for Disease Control (CDC), there are 1.7 cases / 1 million people, the disease is rare, often encounters sporadic cases, very rarely causes epidemics. However, the disease has a very high mortality rate.
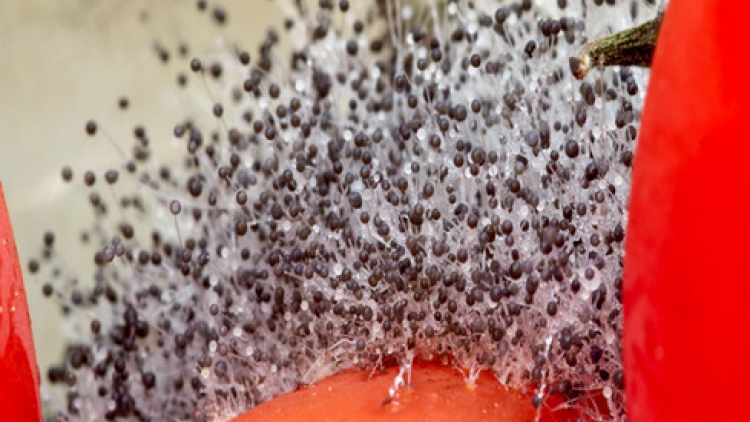

Black fungus also known as Mucomycosis (formerly known as Zygomycosis) is an invasive infection characterized by infarction and tissue necrosis, lesions often black.
According to estimates by the US Centers for Disease Control (CDC), there are 1.7 cases / 1 million people, the disease is rare, often encounters sporadic cases, very rarely causes epidemics.
The disease has a very high mortality rate, the overall mortality rate is up to 54%, this rate varies depending on the type of fungus causing the disease and the location of the infection (the mortality rate is due to sinus infection 46%, lung infection). 76%, disseminated infection 96%).
Mucormycetes are present throughout the environment, especially in soil, and bind to decaying organic matter, such as leaves and animal manure.
They are more common in the soil than in the air, and in summer and fall rather than winter or spring. Most people are exposed to microscopic fungal spores every day, so it may not be possible to completely avoid exposure to mucormycetes.
These fungi are not harmful to most people. However, for people with weakened immune systems, inhaling mucormycete spores can cause a lung or sinus infection that can spread to other parts of the body.
Most people are exposed to microscopic fungal spores every day, so it may not be possible to completely avoid exposure to mucormycetes.
Clinical symptoms vary depending on the affected organ. Patients may experience chest pain, difficulty breathing, coughing up blood, headache, blurred vision, pain in the eye sockets, etc.
Starting antifungal therapy as soon as possible results in a marked improvement in mortality. Surgical resection of the lesion should be considered early, to improve survival in clinical studies.
* SOURCE: https://vov2.vov.vn/suc-khoe/canh-bao-benh-nam-den-mucormycosis-41324.vov2








 Facebook
Facebook
 Tweet
Tweet
 Zalo
Zalo




 News
News















 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google